A team from the University of Illinois and the University of California, Berkeley, has demonstrated a new cooling method that can effectively absorb heat from electronic devices simultaneously. The design power within the volume is 7.4 times that of traditional radiators.
Heat is the enemy of electronic product designers and one of the main limiting factors preventing the miniaturization of electronic products. If heat cannot be released from circuits, they will malfunction functionally and sometimes physically.
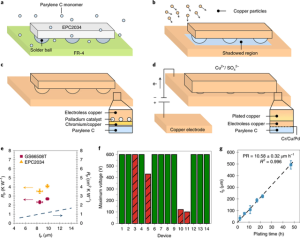
Therefore, heat sinks are a major component of PC cooling technology. Both passive and active cooling use heat spreaders and heatsinks. Common stacked wafer-shaped heat sinks are designed to conduct heat away from sensitive areas and dissipate heat where it won’t cause trouble, but they often fail to dissipate heat from the bottom of the device, where a lot of heat is generated.
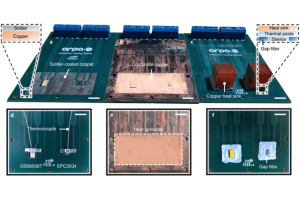
Next-generation heat sinks have been trying to improve on traditional heat sinks. Still, the team says they are often made from expensive materials such as diamond, and they often cannot be mounted directly to the surface of a component.
The team devised a solution that radically improves heat emissions without introducing expensive materials. A latest study published in the peer-reviewed journal Nature Electronics shows a method that “first coats the device with an electrical layer of polychloro-p-xylene film, followed by a copper conformal layer. This puts the copper near the heating element, eliminating the need for a thermal interface material.”
This new copper coating technology can completely cover all exposed surfaces of electronic devices, including the top, bottom and sides. As a unit, the device and heatsink perform as effectively as a heatsink, if not more so, but in a much smaller package. The team successfully tested this ultra-efficient passive cooling method on some gallium nitride power transistors.
Experimental results showed that they recorded impressive results for a single circuit that increased significantly when stacked together.
“Suppose you have multiple printed circuit boards,” said study lead author Tarik Gebrael, a doctoral student at the University of Illinois. “When you use our coating, compared to a traditional liquid or air-cooled heat sink, you can Stack more printed circuit boards in the same volume. That means the power per unit volume is much higher. We demonstrated a 740% increase in power per unit volume.”
Next, the researchers plan to verify the durability of this copper coating, an important step toward industry acceptance. In addition, the researchers plan to conduct tests in immersion cooling and high-pressure environments.

Excellent heat dissipation material – spherical aluminum nitride
Spherical aluminum nitride is a ceramic material with high purity, high thermal conductivity, and high-temperature resistance. Because of its special structure and excellent performance, it has many applications in many fields.
As a heat-dissipation material, spherical aluminum nitride has extremely high thermal conductivity and excellent thermal stability. It can be a heat-dissipation material for high-power electronic devices (such as chips, laser diodes, etc.). It can quickly dissipate heat from the device, effectively reduce its temperature, and improve its stability and life.
Supplier
TRUNNANO is a supplier of spherical aluminum nitride with over 12 years experience in nano-building energy conservation and nanotechnology development. It accepts payment via Credit Card, T/T, West Union and Paypal. Trunnano will ship the goods to customers overseas through FedEx, DHL, by air, or by sea. If you are looking for high-quality spherical aluminum nitride, please feel free to contact us and send an inquiry.
